JMP 9 in 2010 added a new interface for using the R programming language from JMP and an add-in for Excel. The main screen was rebuilt and enhancements were made to simulations, graphics and a new Degradation platform. In March 2012, version 10 made improvements in data mining, predictive analytics, and automated model building. LIMDEP is an econometric and statistical software package with a variety of estimation tools.Download LIMDEP 7.1 Full Version Consists Of Master Software And. LIMDEP: THE PACKAGE LIMDEP Version 9.0 and NLOGIT 4.0 are planned to be released in early summer 2006. The software reviewed here has been finalized; the delay in the release relates to some additions to, and subsequent printing of, the reference manuals. 2.1 Costs The respective single-user costs (U.S. Dollars) are, as of this writing, estimated to be. Java SE 9 Archive Downloads. Go to the Oracle Java Archive page. The JDK is a development environment for building applications using the Java programming language. The JDK includes tools useful for developing and testing programs written in the Java programming language and running on the Java TM platform.
Cite this ItemCopy Citation
Export Citation
Purchase a PDF
How does it work?
- Select the purchase option.
- Check out using a credit card or bank account with PayPal.
- Read your article online and download the PDF from your email or your account.
- Access supplemental materials and multimedia.
- Unlimited access to purchased articles.
- Ability to save and export citations.
- Custom alerts when new content is added.
The American Statistician strives to publish articles of general interest tothe statistical profession on topics that are important for a broad group ofstatisticians, and ordinarily not highly technical. The journal is organizedinto sections: Statistical Practice, General, Teacher's Corner, StatisticalComputing and Graphics, Reviews of Books and Teaching Materials, andLetters.
Building on two centuries' experience, Taylor & Francis has grown rapidlyover the last two decades to become a leading international academic publisher.The Group publishes over 800 journals and over 1,800 new books each year, coveringa wide variety of subject areas and incorporating the journal imprints of Routledge,Carfax, Spon Press, Psychology Press, Martin Dunitz, and Taylor & Francis.Taylor & Francis is fully committed to the publication and dissemination of scholarly information of the highest quality, and today this remains the primary goal.
This item is part of a JSTOR Collection.
For terms and use, please refer to our Terms and Conditions
The American Statistician © 2006 American Statistical Association
Request Permissions
Order by request
Ab einer bestimmten Bestellmenge stellen wir Ihnen ein individuelles Angebot zusammen.
Dieser Artikel wird Ihrem Warenkorb beigelegt, wird jedoch nicht in der Berechnung berücksichtigt
LIMDEP is the econometric software for estimation of linear- and nonlinear-, cross-over-, time-series- and panel-models. Since the beginning LIMDEP was an innovator especially for panel-data-analysis and discrete choice models. It is frequently used especially in the academic world.
In LIMDEP the model complexity is only limited by your imagination and your computers memory. LIMDEP allows you to model brand preferences via Logit-, Probit-, Tobit- and discrete-choice models. Apart from (multinomial) logistic regression the software is a powerful tool for time series analysis.
LIMDEP can be extended by even more specialized functions via the addon NLOGIT.
Arguments for Limdep:
- Number one software for time series analysis
- Innovator for panel-data-analysis
- Discrete Choice Modeling
Recommended products
Stata SE
NLOGIT (includes Limdep)
EViews 12
LIMDEP
LIMDEP is an integrated program for estimation and analysis of linear and nonlinear models, with cross section, time series and panel data. LIMDEP has long been a leader in the field of econometric analysis and has provided many recent innovations including cutting edge techniques in panel data analysis, frontier and efficiency estimation and discrete choice modeling. The collection of techniques and procedures for analyzing panel data is without parallel in any other computer program available anywhere. Recognized for years as the standard software for the estimation and manipulation of discrete and limited dependent variable models, LIMDEP 10 is now unsurpassed in the breadth and variety of its estimation tools.
The main feature of the package is a suite of more than 100 built-in estimators for all forms of the linear regression model, and stochastic frontier, discrete choice and limited dependent variable models, including models for binary, censored, truncated, survival, count, discrete and continuous variables and a variety of sample selection models. No other program offers a wider range of single and multiple equation linear and nonlinear models.
LIMDEP is a true state-of-the-art program that is used for teaching and research at thousands of universities, government agencies, research institutes, businesses and industries around the world.
LIMDEP is a Complete Econometrics Package
LIMDEP takes the form of an econometrics studio. Analysis of a data set is done interactively in a set of windows. Program control may be from a 'script' or in an unstructured session of instructions and manipulations. The program is designed to allow easy setup of data for estimation, specification of different forms of the models, experimentation with different specifications, hypothesis testing, analysis of data and model results and construction of special procedures and estimators.
LIMDEP offers a complete set of tools for econometric analysis. In addition to the estimation programs, LIMDEP provides:
- Data management, including input from all standard sources (such as Excel), all manner of transformations and sample controls
- Built-in estimation programs plus a programming language, matrix algebra package and scientific calculator that allow you to write your own estimators, test statistics and simulation and analysis programs
- Random number, vector and matrix capabilities for bootstrapping, Gibbs sampling and Monte Carlo simulation
- A wide range of graphical and numeric descriptive statistics capabilities
- Optimization tools that allow you to construct your own likelihood, GMM, or maximum simulated likelihood estimators
- Analysis tools including graphics, numerical analysis and post estimation tools for specification and hypothesis testing
- The new electronic documentation with over 2,500 pages contains full reference guides for the program, background econometrics, and sample applications.
Further Information
System Requirements for the Software Limdep
| Windows® | |
| Further Requirements | |
| Operating System | Windows XP, Vista, 7, 8, 10 |
| Min. CPU | 486 Processor or better |
| Min. RAM | 512 MB |
| Disk Space | 100 MB |
LIMDEP Version 11 continues the expansion of our premier software for cross section, panel data and time series analysis. Version 11 contains major new extensions to the program for estimation and statistical analysis of econometric models and a long list of new models and features. New features include:
Stochastic Frontier Models
- New parametric specifications
- Normal-Rayleigh
- New FIML estimator for sample selection correction
- Sample selection with panel data
- Partially inefficient latent class stochastic frontier model
Panel Data Stochastic Frontier Models
- Rayleigh model
- Belotti and Ilardi partial differences
- True fixed and random effects
- Wikstrom method of moments
- Generalized true random effects
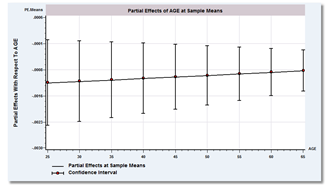
New Partial Effects and Simulation Tools
- New graphical devices
- Transition matrices for categorical variables
- Krinsky and Robb method for standard errors
- Extended to more models
Expanded Graphics
Histograms
- Overlay histograms with box plots or kernel density estimators
- Group up to 4 histograms
Box Plots
- Up to 40 plots in one figure
- New BOXPLOTS command
- Simultaneous plots
Bubble Plots
Kernel Density Estimator
- Several new specifications for plotting kernel density estimators
- Simultaneous plots
Treatment Effects Procedures
- Endogenous treatment effects
- FIML estimation for probit, ordered probit, Poisson and negative binomial
New Tools for Estimation and Inference
New Analysis Tools
- Over 30 new CREATE functions for panel data transformations
- Dozens of new functions for CALCULATE and MATRIX
- New random number generators
More Models and Features
- Cluster covariance matrices for all models
- Inverse hyperbolic sine model
- Fractional regression for cross section and panel data
- New panel data functions for MAXIMIZE
Data Descriptive Devices
- Obtain separate strata means for stratified data
- New commands for correlation matrices
- New TABLE command for descriptive statistics by strata
- New commands for quantiles and frequencies
- New Cronbach’s alpha correlation device
Character Data
- Observation labels
- Labellists
- Observation tags
Loglinear Models
- Generalized beta of the second kind
- Generalized gamma model
Enhanced EXECUTE and Procedures
- New specifications for bootstrap and jackknife iterations
- Block bootstrap for panel data
Comparing Alternative Specifications of a Model
More Features

Version 10 contains major new extensions to the program for estimation and analysis of econometric models and a long list of new models and features.
Model Estimation, Analysis and Simulation
- Interactions and Nonlinearities: Models that contain interactions, products, powers and logs of variables are now specified explicitly. The basic command structure is fully integrated throughout the entire program, not just layered on top of a few models. Every specification of every model can use this structure. This will provide a significant convenience in the specification of models. But, the major benefit of this explicit format comes in terms of how it enables you to obtain partial effects and simulations for your models.
- Partial Effects: Partial effects, using the sample averages of the effects or calculations at the means of the data, can be computed automatically for any variable in any model regardless of how intricate. Effects can be simulated for specified values or ranges of variables, and tabulated or plotted with confidence intervals. The lack of appropriate calculations of partial effects for models that contain interactions and nonlinearities has been recognized as a major shortcoming of software and of many published analyses. LIMDEP's new PARTIAL EFFECTS command solves this problem. This feature can be used with all models fit by LIMDEP, or with a function of your own that need not be part of any built in model in the program. This feature will change the way you analyze nonlinear models.
- Model Simulation and Oaxaca Decomposition: The partial effects feature can also be used to simulate the prediction function (usually the conditional mean) for any model fit by LIMDEP, or any model or equation that you wish to specify in the SIMULATE command. Simulations can involve scenarios, such as tracing the sample average prediction of a probability or a count of outcomes as a function of age. The simulation feature is also useful for computing Oaxaca decompositions for subgroups of the sample. Like PARTIAL EFFECTS and SIMULATE, DECOMPOSE is used with all models built into LIMDEP, or with a function or model that you specify yourself.
- Multiple Imputation: The technique of multiple imputation for handling missing data has been gaining popularity. LIMDEP's new implementation of this technique is woven into the entire program, not just a few specific models. Any estimator, even your own created with MAXIMIZE, or any other computation involving data that produces a coefficient vector and a sampling covariance matrix, can be based on multiple imputed data sets. And, we have built this technique to bypass the need to create multiple data sets - traditionally, the need to replicate the full data set has hobbled this method. LIMDEP's implementation of multiple imputation uses only the existing data set. The results are fully replicable as well. (You can create and save the imputed data sets if you wish.)
Extensions of Estimation and Analysis Methods
- Streamlined output with additional test and diagnostic statistics
- Restrictions and hypothesis tests in all models
- Simpler natural format for model specification
- Single step estimation for testing multiple hypotheses
- Numerous new features for user written iterative and looping procedures
- New Wald features for computing standard errors
- Sample average functions as an alternative to computing functions at the means of the data
- Variances using the delta method account for the averaging procedure
- Multiple new functions for matrix algebra program
- Expanded graphics capabilities
- New additions for kernel density estimation, including plotting multiple KDEs in the same figure
- Contour plots
- Enhanced tools for creating and labeling graphs
- Robust covariance estimators for linear models
- Jackknife and bootstrap estimators for standard errors and confidence intervals and for large sample behavior of test statistics
- Extension of panel data to nearly all model frameworks
New Models and Data Analysis Settings
- Models for count data
- Zero truncation for count data models with panel data
- NB-X - negative binomial model for underdispersion
- NB-E - negative binomial model with endogenous truncation (on site sampling)
- Poisson and negative binomial models with endogenous treatment effects
- Poisson - inverse gauss mixture
- Generalized Poisson with zero inflation and 1/2/P nested functional forms
- Count data hurdle models with endogenous participation
- Non- and semiparametric regression models
- Lowess nonparametric regression
- QREG for quantile regression
- QCREG for quantile regression for count data
- LIML estimator for regression with endogenous RHS variables
- Binary and ordered choice
- Ordered probit with endogenous treatment effects
- Generalized ordered choice with random parameters and thresholds
- Fractional response model for panel data
- Arc tangent model for binary choice
- Stochastic frontier
- FRONTIER with nonparametric frontier function
- Battese-Coelli panel data frontier models
- New automated tools for specification tests and calculations such as technical efficiencies
- MAXIMIZE/MINIMIZE with random parameters
- Numerical Analysis
- FUNCTION to plot and simulate any specified function
- SOLVE to locate the solutions to f(x)=0
Program Limits at a Glance
We are often asked about LIMDEP's specific internal limits. The following limits are relevant to the most common applications.
- Active Data Set
- Variables: 900
- Observations: 3,000,000+
- Total cells in data area: limited by memory
- Namelists: 25
- Variables in namelist: 100
- Command Entry
- Characters in one command: 10,000
- Characters in a stored procedure: 10,000
- Commands in a stored procedure: 100
- Stored procedures: 10
- Model Size, General & Specific
- Number of parameters: 150
- Equations for SURE & 3SLS: 30
- Equations for WALD, NLSURE, GMM: 50
- Panel Data Models
- Groups in fixed & random effects:
- Linear models: unlimited
- Nonlinear models: 100,000
- Regressors in fixed & random effects: 150
- Periods in linear effects: 1,000
- Groups x Regressors: unlimited
- Groups in fixed & random effects:
- Periods in fixed effects (Chamberlain) logit: 100
- Matrix & Scalar Algebra
- Number of active matrices: 100
- Number of active named scalars: 100
- Size of a matrix: 50,000 cells
Model Estimation and Analysis
Over 100 model formulations for continuous, discrete, limited and censored dependent variables are provided, including:
- Linear and nonlinear regression
- Robust estimation
- Binary choice
- Ordered choice models
- Unordered multinomial choice
- Censoring and truncation
- Sample selection models
- Count data
- Loglinear models
- Stochastic frontier and DEA
- Survival analysis
- Quantile regression (linear and count)
- Time series models
- Panel data models
Data Description and Graphics
Descriptive statistics and graphical analysis tools include:
- Descriptive statistics for cross sections and panels
- Tables of means and quantiles
- Time series
- Spectral density
- Graphics tools
- Kernel density
- Discriminant analysis
- Contour plots
Count Data
The widest range of specifications for count data of any package is provided, including several newly developed models:
- Poisson and negative binomial models
- New specifications for NB models
- Gamma, generalized Poisson, Polya-Aeppli
- Zero inflation and hurdle
- Fixed and random effects
- Latent class
- Quantile Poisson regression
Data Environments
Nearly every model may be extended to a variety of frameworks including:
- Data transformations
- Multiple imputation
- Cross section
- Panel data
- Time series manipulation

Programming and Numerical Analysis
Programming language including matrix and data manipulation commands is provided for building new estimators:
- MAXIMIZE/MINIMIZE for user supplied functions
- Matrix programming with LIMDEP
- Scientific calculator
- Numerical analysis tools, integration and differentiation
- Simulation based estimation
- Program Gibbs samplers
Frontier and Efficiency Analysis
All forms of the stochastic frontier model are provided:
- Fixed and random effects
- True fixed and random effects
- Latent class stochastic frontier
- Battese and Coelli
- Heteroscedasticity
- Technical inefficiency estimation
- Data envelopment analysis (This is the only package with both SFA and DEA.)
Discrete Choice Models in LIMDEP
Discrete choice estimators for binary, multinomial, ordered, count and multivariate discrete data are provided:
- Binary choice - dozens of specifications
- Ordered choice
- Hierarchical ordered choice
- Panel data
- Multinomial logit
- Count data models
- Bivariate binary and ordered choice
- Discrete choice with sample selection
Time Series Analysis
A range of estimators for time series are provided including:
- ARMAX models
- GARCH and GARCH-in-mean models
- Spectral density estimation
- ACF and PACF
- Phillips-Perron tests
- Newey-West estimator
Accuracy
Extremely accurate computational methods are employed throughout. High marks are earned on all National Institute of Standards and Technology test problems, including:
- Descriptive statistics
- Analysis of variance
- Linear regression
- Nonlinear least squares
Post Estimation
Extensive tools for post estimation enable manipulation of model results along with other statistics and procedures.
Data Management
Limdep 9 New Version Free Download
Data management tools are provided for input of data or internal generation with the random number generators, including:
- Data transformations
- Sampling and bootstrapping
- Bootstrap cross section observations or panel groups
- Weighted data
- Random number generation
- Cluster sampling and stratification
Multiple Imputation
Limdep 9 New Version
Multiple Imputation is used to generate proxies for missing values in order to use information from the model and within the sample to increase the precision of estimators. Missing values for continuous, binary, count, Likert, fractional and multinomial data may be generated. Results from multiple samples are generated and averaged to produce the final results.
LIMDEP Documentation
The LIMDEP documentation with over 2,500 pages, contains full reference guides for the program, background econometrics, and sample applications. The LIMDEP documentation consists of two guides:
LIMDEP Reference Guide
The LIMDEP Reference Guide provides all instructions for operating the program, including installation, invocation, and most of the basic setup operations that precede model estimation. These operations include reading and transforming data and setting the sample. This manual also describes the optimization procedures, how to use the matrix algebra package and scalar scientific calculator as stand alone tools and as part of LIMDEP programs, what types of results are produced by the program, and some of the common features of the model estimation programs, such as how to do post estimation analysis of model results, including partial effects and simulation. The LIMDEP Reference Guide also includes a complete listing of the program diagnostics.
LIMDEP Econometric Modeling Guide
The LIMDEP Econometric Modeling Guide provides the econometric background, LIMDEP commands, and examples with data, commands and results. Topics are arranged by modeling framework, not by program command. There are chapters on
- Descriptive statistics
- Linear regression
- Panel data analysis
- Heteroscedasticity
- Binary choice models
- Models for count data
- Censored and truncated data
- Survival models
- Nonlinear regression
- Time series models
- Nonlinear optimization
- Sample selection models
and many others. Each model fit by the program is fully documented. The full set of formulas for all computations are shown with complete mathematical documentation of the models. Additional chapters in this guide show how to do numerical analysis and how to program your own estimators.



